Are you studying to become a pharmacist? You’re probably well-aware that the North American Pharmacist Licensure Examination (NAPLEX) stands in your way. One of the medications you’ll be tested on is Digoxin. Check out this video explanation from MedCram of a practice question on Digoxin found in the BoardVitals NAPLEX Question Bank.
The Question:
A 70-year-old male with a history of diabetes, GERD, and COPD develops atrial fibrillation with a rapid rate. After cardioversion, he begins treatment with digoxin. Which of the following is true of treatment with digoxin? (Select all that apply.)
A. Oral loading with digoxin results in a steady state concentration in 3-4 days.
B. Patients who take antacids may require an increase in dosage. (Correct)
C. Digoxin has a broad therapeutic window.
D. Patients with hypokalemia should not take digoxin until the serum potassium is normal.
E. The desired serum concentration of digoxin in patients with atrial fibrillation is 0.5 to 0.9 ng/mL. (Correct)
Correct Answer: (B, E) Patients who take antacids may require an increase in dosage; The desired serum concentration of digoxin in patients with atrial fibrillation is 0.5 to 0.9 ng/mL.
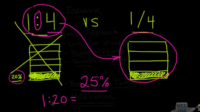
Explanation: Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside that is used clinically to treat heart failure due to systolic dysfunction and to treat certain supraventricular tachyarrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation. Digoxin works in atrial fibrillation by slowing conduction through the AV node by increasing vagal tone. It has a narrow therapeutic window and toxicity may be life threatening, including cardiac arrhythmias. Serum concentration should be monitored closely, particularly in patients with renal insufficiency. Some medications, including quinidine, verapamil, and amiodarone can increase serum digoxin levels. Erythromycin and tetracycline may impair gastrointestinal digoxin metabolism, also leading to higher serum digoxin concentration. Antacids can decrease the intestinal absorption of digoxin, requiring an increase in dose to achieve the desired level. In atrial fibrillation, experts recommend a level of 0.5 to 0.9 ng/mL.**
** Digoxin is only the treatment of choice in patients with heart failure and the therapeutic level list is 0.5 – 0.9. The American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association 2013 Guidelines for the management of heart failure gave the same range (0.5-0.9).
(A) Incorrect. Digoxin can be rapidly loaded intravenously or can be loaded orally with a steady state achieved in 7-10 days with oral loading in most patients. (C) Incorrect. Digoxin has a narrow therapeutic window with potentially
(C) Incorrect. Digoxin has a narrow therapeutic window with potentially life-threatening toxicity.
(D) Incorrect. Patients with hypokalemia and other electrolyte disorders are more likely to experience a digoxin-associated arrhythmia, so the serum digoxin levels in these patients should be monitored closely until serum potassium returns to normal range.
The NAPLEX Practice Question bank has more than 1400 questions with detailed explanations and references targeted to the NAPLEX exam. These practice questions include calculations, fill in the blank and multiple choice questions, similar to what you will find on the exam. Want more free practice? Start with a free trial.